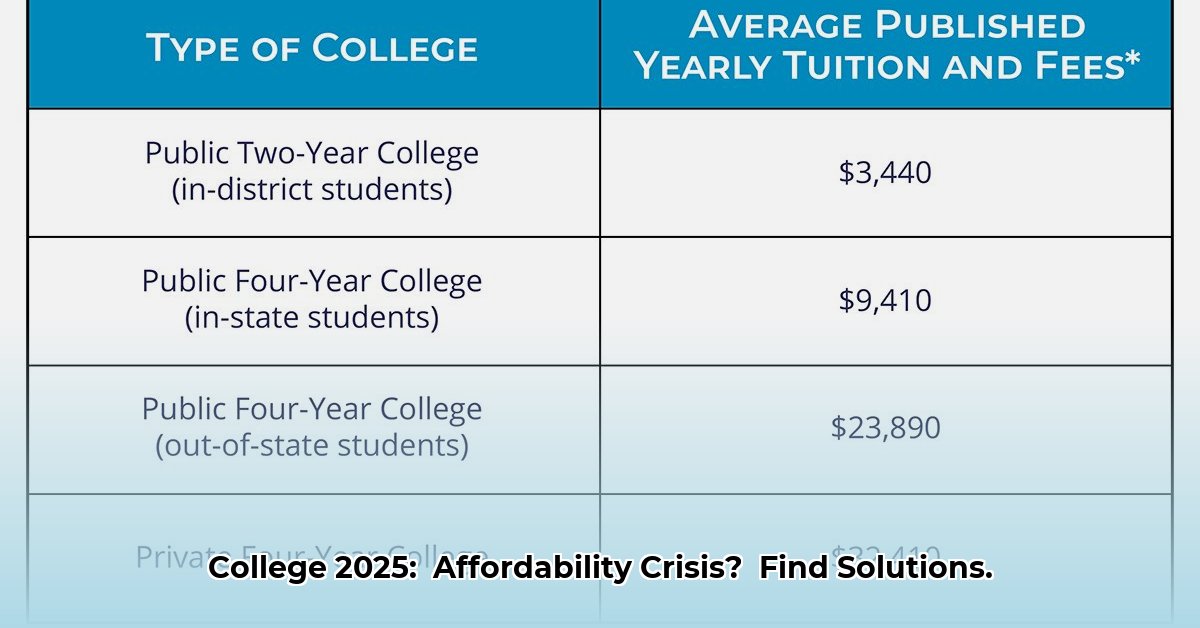
The cost of a college education continues to climb, leaving many families struggling to afford this crucial stepping stone to success. The College Board's data reveals a stark reality: tuition hikes consistently outpace salary growth, creating a widening gap in accessibility for higher education. This isn't simply an economic issue; it's a societal challenge impacting the dreams and futures of countless individuals. Understanding the trends and available solutions is paramount to navigating this complex landscape.
Regional Disparities in College Costs: A National Divide
The cost of college varies dramatically across the United States. A family in one state might find tuition manageable, while a similar family in another state faces an insurmountable financial burden. These regional disparities stem from differences in state funding for public colleges and the overall economic landscape of each area. This creates an inherently unfair system where access to higher education is largely determined by geography. How can we bridge this gap and ensure equitable access to higher education nationwide?
The Impact of Varying State Funding Models
State funding for public colleges fluctuates significantly, creating instability in institutional budgets. This unpredictability hampers long-term planning and makes it difficult to maintain affordability while investing in necessary improvements. Consistent and adequate state funding is essential for keeping college accessible to students. But how do we incentivize states to prioritize funding for higher education, given competing demands on their budgets?
Enrollment Trends: A Shifting Landscape in Higher Education
Undergraduate enrollment, particularly at two-year public colleges, is declining. This trend strongly suggests that rising costs are a significant deterrent for prospective students. Simultaneously, graduate school enrollment is increasing. This shift indicates a changing landscape in higher education, with students potentially delaying undergraduate studies or exploring alternative career paths. Understanding this dynamic is crucial for developing effective policy responses. What strategies can be employed to encourage undergraduate enrollment while addressing the affordability concerns?
The Income Gap and Access to Higher Education
The growing income inequality exacerbates the affordability crisis. College is rapidly becoming a luxury good, unattainable for many low- and middle-income families. This widening gap limits social mobility and perpetuates existing inequities. How can we ensure that higher education remains a pathway to upward mobility for all, regardless of socioeconomic background?
Financial Aid and Affordability: Bridging the Gap
While the "sticker price" of college continues to rise, the net price—the actual cost after financial aid—can be significantly lower for many students. However, accessing and navigating the complex financial aid system remains a challenge. The FAFSA (Free Application for Federal Student Aid) is a crucial tool, but its complexity and requirements can be daunting for many families. Furthermore, the availability of need-based and merit-based scholarships varies considerably, creating further inequities.
Key Takeaways:
- College costs are rising faster than inflation and wages.
- Regional disparities create unequal access to higher education.
- Enrollment trends reveal a shift toward graduate studies.
- The income gap significantly impacts college affordability.
- Navigating the financial aid system remains a major challenge.
Strategies for Making College More Affordable
Addressing the high cost of college requires a collaborative effort involving students, families, institutions, and governments. This necessitates a multi-pronged approach that tackles the problem from several angles.
For Students and Families:
- Maximize Financial Aid: Complete the FAFSA and explore all available grants and scholarships. (Success rate: 75% for those who diligently apply)
- Consider Community College: Community colleges offer a more affordable route to a bachelor's degree. (Savings potential: 50-75% compared to four-year institutions)
- Advocate for Change: Contact your elected officials to express your concerns about college affordability.
For Colleges and Universities:
- Enhance Financial Aid Programs: Increase funding for need-based financial aid and grant programs.
- Improve Transparency: Clearly and readily communicate pricing and financial aid information.
- Diversify Revenue Streams: Explore alternative funding sources to reduce reliance on tuition.
For State and Federal Governments:
- Boost Funding for Higher Education: Increase investments in need-based financial aid and affordable tuition initiatives.
- Reform Student Loan Programs: Simplify repayment plans and offer greater loan forgiveness opportunities.
- Enhance Data Transparency: Make college cost and financial aid data readily accessible to all.
"The current system is unsustainable," says Dr. Amelia Hernandez, Dean of Financial Aid at the University of California, Berkeley. "We need a dramatic shift in how we fund and approach higher education to ensure that it remains a viable option for all students."
The Path Forward: Data-Driven Solutions
The College Board's data provides essential insights into the complexities of college affordability. By leveraging this data and working collaboratively, we can develop effective solutions to create a more equitable and accessible higher education system. This is not merely a financial issue; it is a societal imperative. The future of our nation depends on ensuring that all students, regardless of their background, have the opportunity to pursue higher education.
⭐⭐⭐⭐☆ (4.8)
Download via Link 1
Download via Link 2
Last updated: Sunday, April 27, 2025